posix 目录下
CFLAGS+= -pthread
LDFLAGS+=-pthread创建函数
- 参数:获取创建的线程的标识 回填,并且指定线程的属性 一般默认 空。一个兄弟线程,aka函数,传的参数通过第四个参数来传。`int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread,const pthread_attr_t *attr,void *(*start_routine)(void *),void *arg);
- void*最好用,传地址过去,做成一个结构体,可以混合传递(整形 浮点型)
- 它的返回值是error number 当出错的时候。而不是返回值为-1,自己设置error number.
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<pthread.h>
static void *func(void *p)
{
puts("Thread is working!");
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
int err;
puts("Begin!");
err=pthread_create(&tid,NULL,func,NULL);
if(err)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create():%s\n",strerror(err));
exit(1);
}//将来可以重定向流
puts("End!");
exit(0);
}
- 诡异的是看不到,线程的调度取决于调度器的调度策略
- main线程,创建的线程 还没有被调度 main就exit了,进程正常终止的方式之一。
线程 终止
看函数 pthread_exit
static void *func(void *p)
{
puts();
pthread_exit(NULL);
//return NULL;
//做线程栈的清理。相比于 return NULL
}线程的收尸 pthread_join
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
puts("End");pop给你一个选择是否执行 int execute
栈的清理
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib,h>
#include<pthread.h>
static void cleanup_func(void *p)
{
puts(p);
}
static void *func(void *p)
{
puts("Thread is working!")
//栈的清理
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_func,"cleanup:1");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_func,"cleanup:2");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_func,"cleanup:3");
puts("push over!");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
puts("Begin!");
err=pthread_create(&tid,NULL,func,NULL);
if(err)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create():%s\n",stderror(err));
exit(1);
}
puts("End!");
exit(0);
}
其实 这两个方法 是宏 不是 函数
gcc cleanup.c -E预处理 处理掉所有以#开头 do 半个括号 另外半个括号在另一个宏 pop中,
do 半个括号 另外半个括号在另一个宏 pop中,
push 和pop要成对出现,
static void *func(void *p)
{
puts("Thread is working!")
//栈的清理
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_func,"cleanup:1");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_func,"cleanup:2");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_func,"cleanup:3");
puts("push over!");
pthread_cleanup_pop(1);
pthread_cleanup_pop(1);
pthread_cleanup_pop(1);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
pop 弹出来的时候调用 1 表示调用 0 表示不调用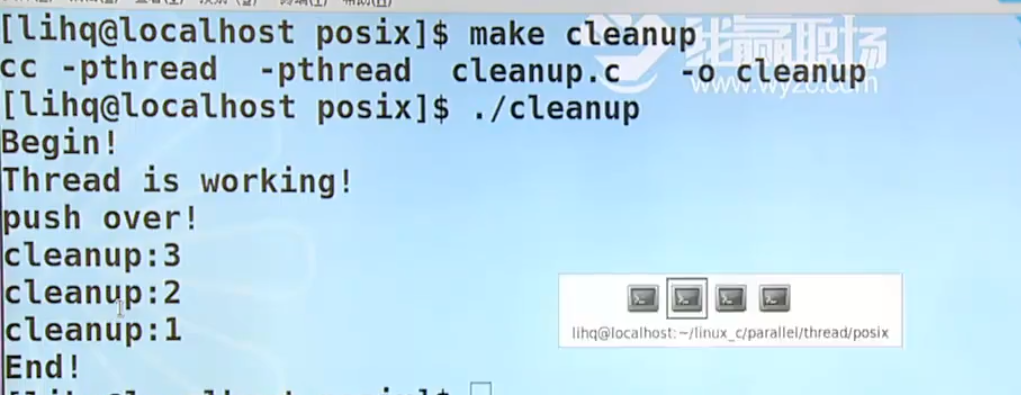
线程的取消 发送一个取消请求
成功打开
钩子函数挂关闭文件操作 打开完了挂一个钩子函数 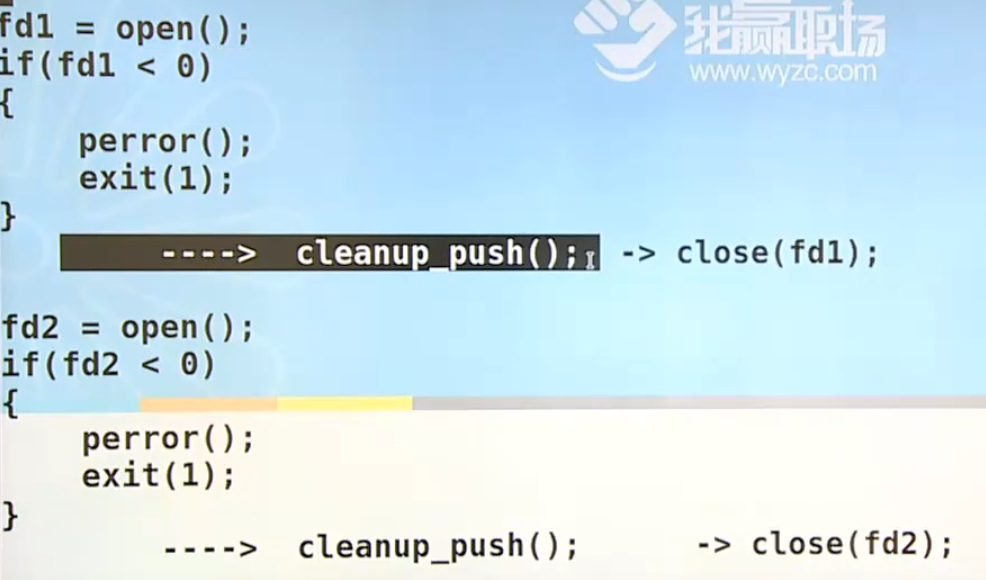
cancel 有关的函数 setcanceltype setcancelstate