- 行为建模描述了电路的行为
coding guidelines
- use blocking(immediate) assignments for combinational circuits
- use nonblocking (deferred) assignments for registers
- assign a variable only in a single always block
- separate memory components(registers) into individual code segments
- describing a synchronous system ,make sure registers are written in their own always statement,the output logic is written in its own always statement
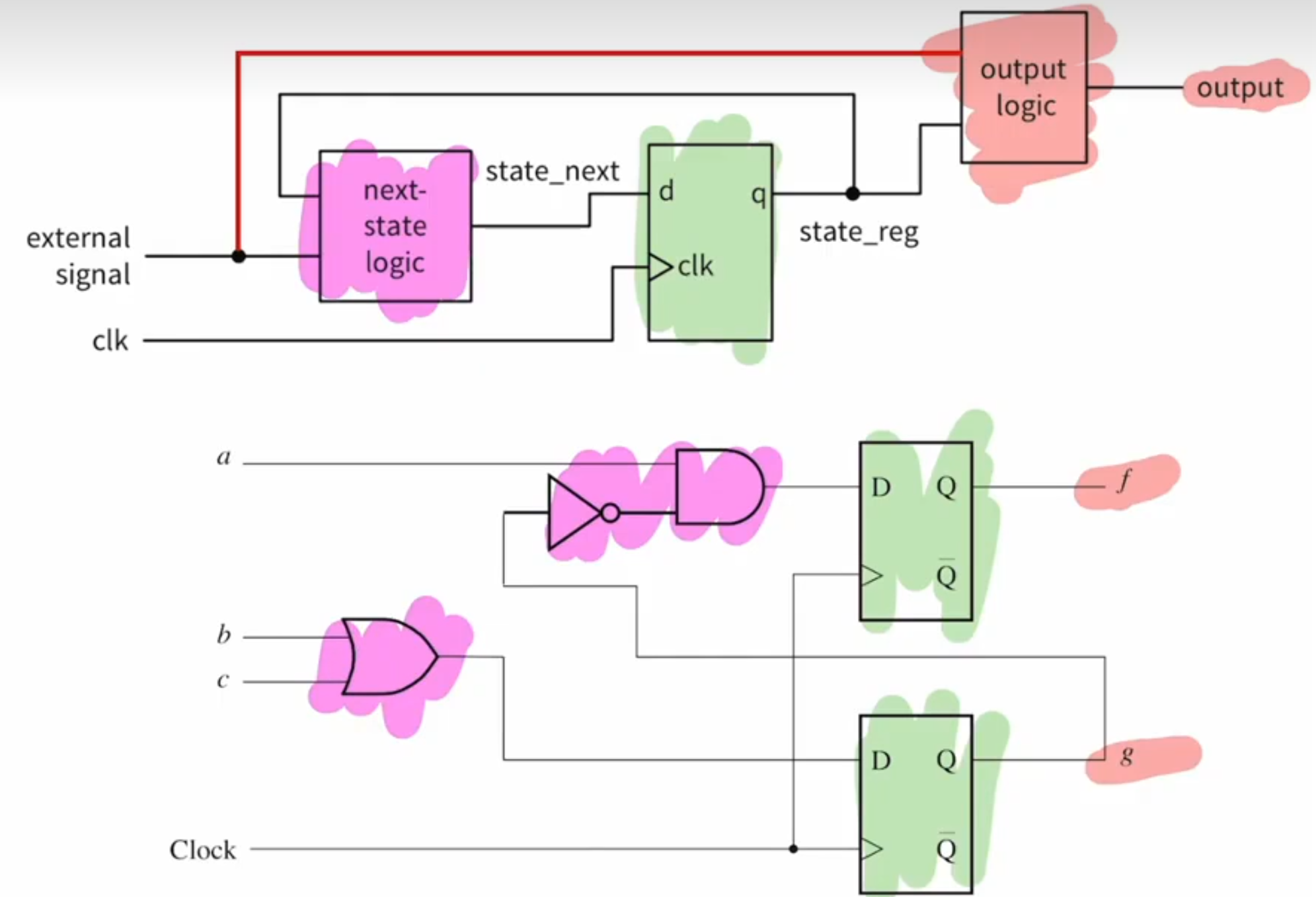
module coding_guidlines{ input a,b,c, input clk, output f,g }; reg f_reg,f_next,g_next,g_reg; //出 reg,入 next //flip floop always @(posedge clk) begin f_reg<= f_next; g_reg<=g_next; end //next state logic always @(*) //sensitive list 或者 a, b ,c, g_reg begin f_next=a & ~g_reg; g_next=b |c; end //out put logic assign f=f_reg; assign g=g_reg; endmodule - describing a synchronous system ,make sure registers are written in their own always statement,the output logic is written in its own always statement
- 将 input logic state logic output logic分开
简洁的写法
module coding_guidlines{
input a,b,c,
input clk,
output f,g
};
always @(posedge clk)
begin
f<=a&~g;
g<=b|c;
end
endmodule多出来的寄存器,创建了不需要的额外的锁存器 寄存器
module coding_guidlines{
input a,b,c,
input clk,
output f,g
};
reg ag,bc;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
ag<=a&~g; //f需要的是之前的ag的值 而不是现在的值
f<=ag;
bc<=b|c;
g<=bc;
end
endmodulemodule coding_guidlines{
input a,b,c,
input clk,
output f,g
};
always @(posedge clk)
begin
ag=a&~g; //f需要的是之前的ag的值 而不是现在的值
f<=ag;
bc=b|c;
g<=bc;
end
endmodule先前的值和一个新的值 需要某种寄存器来存储